Wellness Club — Blood Pressure and Hypertension: What You Should Know
Abingdon, VA. -
Saturday, Feb 1, 2025.
Written by: Rebecca Webb, PharmD, Pharmacy Clinical Services Manager
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the amount of force that blood is pushing against the walls of your arteries (blood vessels) as they carry blood from your heart to the other parts of your body. It is measured in millimeters of mercury, which is abbreviated mmHg. Blood pressure is represented by two numbers:
• Systolic blood pressure reading (first number or top number) - measures the pressure pushing against artery walls when your heart beats.
• Diastolic blood pressure reading (second number or bottom number) - measures the pressure pushing against artery walls between heartbeats.
What is a normal blood pressure reading?
According to the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA), a normal blood pressure reading is below 120/80 mmHg. However, blood pressure goals can be specific to the individual. Your healthcare provider (e.g., primary care provider) should talk with you about your blood pressure goals.
What is hypertension?
High blood pressure is also known as hypertension. The ACC and the AHA state that hypertension is blood pressure consistently 130/80 mmHg or greater.
Many individuals are not aware they have high blood pressure. There are typically no symptoms. This is why high blood pressure is often called a ‘silent killer.’
Almost half of U.S. adults have hypertension. Only about a quarter of these individuals have their blood pressure under control.
How does uncontrolled high blood pressure threaten your health?
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can be a threat to your health over time. It can result in:
• Stroke
• Heart attack
• Heart failure
• Heart disease
• Kidney disease
• Loss of vision
• Atherosclerosis (i.e., buildup of plaque in your arteries causing them to narrow)
• Other dysfunctions
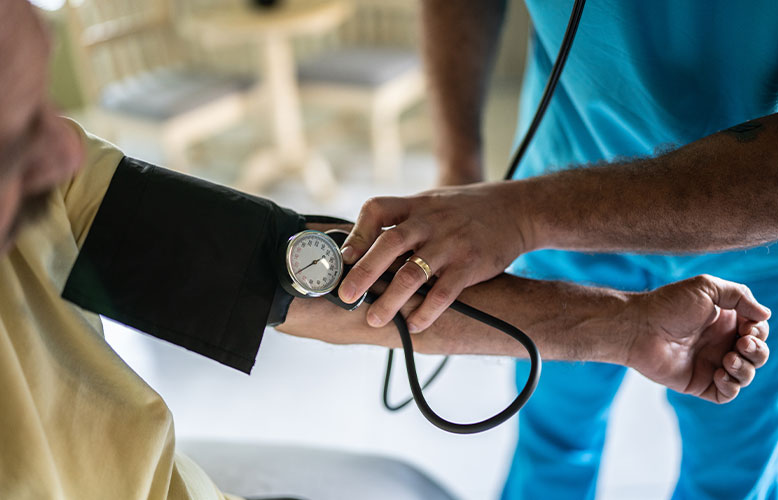
How and when should you monitor your blood pressure?
When you visit your healthcare provider, your blood pressure is typically one of the first measurements taken during your appointment. If you have hypertension, it is also recommended to monitor your blood pressure routinely at home. Keeping a blood pressure journal to share with your healthcare provider at visits is essential for optimal hypertension management. Talk with your healthcare provider to see how often you should record your blood pressure at home.
Outside of a healthcare setting, an automatic home blood pressure monitor (e.g., cuff-style, upper arm) can be used to track your readings. Talk to your Food City Pharmacist if you have questions or need to purchase a home blood pressure monitor. Knowing the correct cuff size and having the cuff fit properly are imperative for an accurate reading. Our pharmacists can offer many tips to help ensure you are getting the most precise blood pressure measurements at home. Food City Pharmacies also have blood pressure kiosks where you can check your blood pressure reading for free at your convenience.
Is medication adherence important for controlling high blood pressure?
Lifestyle modifications (e.g., eating a healthy diet, exercising routinely, limiting alcohol consumption, not smoking, keeping a healthy weight, managing stress, etc.) are necessary for controlling blood pressure. However, many individuals also need prescription medications to reach their blood pressure goals. In fact, four out of five U.S. adults with hypertension are prescribed medications to help manage their blood pressure.
Medication adherence is crucial to optimal blood pressure control for patients with hypertension. Know when and how to take your blood pressure medication(s). Incorporate medication taking into your daily routine (e.g., take when brushing your teeth, take at mealtime, take at bedtime, etc.). Use adherence tools, such as pill boxes, mobile apps, alarms, or automatic refills at the pharmacy. If you have concerns about the side effects, costs, or benefits of your medication(s) for hypertension, talk with your Food City Pharmacist. Do not stop taking your blood pressure medication(s) without consulting your healthcare provider.
References:
1. Blood pressure chart: What your reading means. Mayo Clinic website. Blood pressure chart: What your reading means - Mayo Clinic. Accessed January 13, 2025.
2. Estimated Hypertension Prevalence, Treatment, and Control Among U.S. Adults. Million Hearts website. https://millionhearts.hhs.gov/data-reports/hypertension-prevalence_2018.html. Accessed December 20, 2024.
3. High Blood Pressure Facts. Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC) website. https://www.cdc.gov/high-blood-pressure/data-research/facts-stats/index.html#print. Accessed December 20, 2024.