Wellness Club — Preventing and Treating Bug Bites
Abingdon, VA. -
Monday, Jun 1, 2020.
by Rebecca Webb, PharmD Pharmacy Clinical Services Manager, K-VA-T Food Stores
As summer approaches, warmer weather means spending more time outdoors. Enjoying time outside can lead to encountering pesky bugs, such as mosquitoes, ticks, biting flies, or another similar pest. Bites from these bugs can not only be annoying, they can also be dangerous since some spread disease. Therefore, it is a good idea to be informed on how to prevent and treat bug bites so you can be prepared and safe when spending time outdoors.
Preventing bug bites
There are general precautions you can take to prevent bug bites. One safeguard is to minimize your exposure by wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, long pants, hats, socks, and closed shoes. An option for additional protection is to treat clothing and gear with an insecticide/ acaricide (kills ticks), such as permethrin. Permethrin should not be applied directly to skin — always follow label instructions when using this product. You can also buy pre-treated clothing and gear.
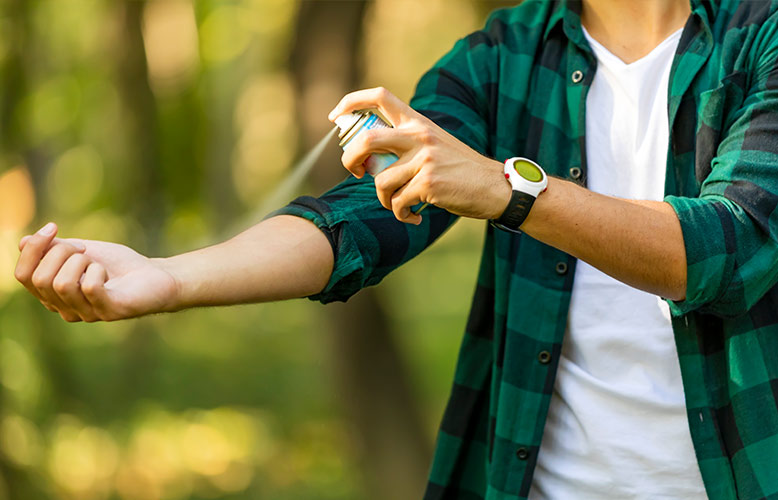
One of the best ways to prevent bug bites is to use insect repellent. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends using Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)-registered skin-applied insect repellents with the active ingredients DEET, picaridin, oil of lemon eucalyptus, IR3535, para-menthane-diol, or 2-undecanone. Examples of brand name products that contain some of these active ingredients include Off!® Deep Woods®, Off!® familycare, Cutter®, Cutter® Skinsations®, Cutter® Backwoods®, and Repel® Sportsmen Formula®. Important information on the safety and efficacy of insect repellents includes:
o Always use as directed per labeling instructions.
o Check age restrictions on products.
o Reapply as stated on directions.
o Do not apply to skin under clothing.
o It should not be used on injured or irritated skin.
o Do not spray directly on your face. Products should not be applied to your eyes or mouth.
o Use an adequate amount to cover exposed skin and clothing. Excessive use is typically unnecessary.
o If you are using sunscreen, apply it first before using the insect repellent. Sunscreen/repellent combination products are not recommended.
o Wash your hands after using the product. Once returning indoors, wash repellent-covered skin with soap and water.
Although not a preventative measure for a bug bite, it is advised to inspect for ticks on your skin, hair, or clothing during and after being outside. Quickly removing an attached tick may help reduce the spread of infection.
Treating bug bites
Despite preventative measures, you may still have the occasional bug bite. The pain, itching, irritation, or minor swelling caused by a bug bite generally eases within one or two days. Most bug bites can be treated at home. Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol®, TopCare® health™ Pain Relief) or ibuprofen (Advil®, Motrin® IB, TopCare® health™ Ibuprofen), can help for painful bites. OTC anti-itch creams, such as hydrocortisone (Cortizone 10®, TopCare® health™ Hydrocortisone 1% Cream), can be helpful for bites that itch. An OTC oral antihistamine, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl® Allergy, TopCare® health™ Allergy Relief), can reduce itching for stronger reactions. Use an ice pack or cool compress to help alleviate swelling from a bug bite.
It is important to always follow the directions on the package labeling of an OTC product. If you have any questions, ask your local Food City pharmacist. Seek medical advice from a health care professional if you have any concerns about a bug bite, even for minor reactions. Promptly contact your doctor if any serious symptoms (i.e., rash, fever, or body aches) occur after a bug bite. If you experience symptoms of a severe allergic reaction, notify emergency care immediately.
References:
1. Repellents: Protection against Mosquitoes, Ticks and Other Arthropods. United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) website. https://www.epa.gov/insect-repellents. Accessed May 19, 2020.
2. Tips to Prevent and Treat Bug Bites. American Academy of Dermatology Association. https://www.aad.org/public/everyday-care/injured-skin/bites/prevent-treat-bug-bites. Accessed May 19, 2020.